Introduction
Neuropsychiatric disorders refer to a wide range of mental health conditions that affect the brain and the way it functions. They include anxiety disorders, mood disorders, psychotic disorders, eating disorders, personality disorders, and many others. These disorders can be very debilitating and have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life.
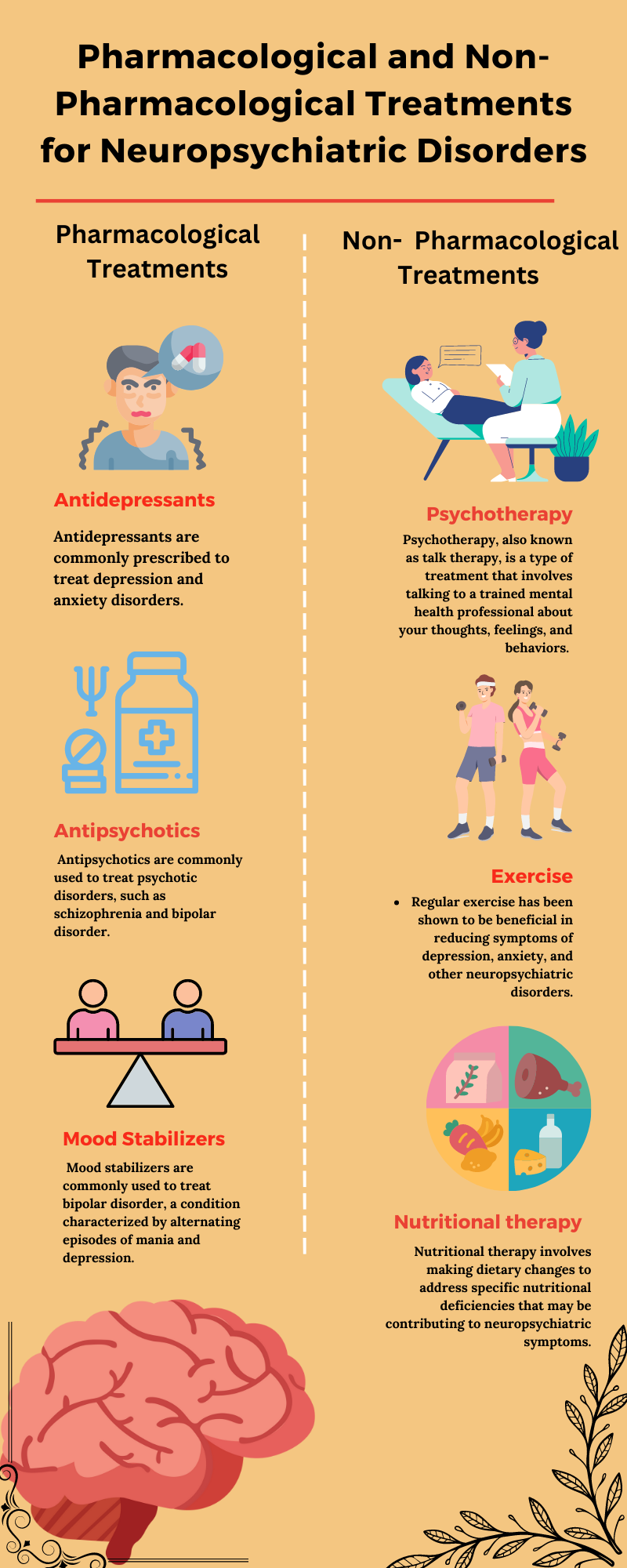
There are two main types of treatments for neuropsychiatric disorders: pharmacological and non-pharmacological. Pharmacological treatments involve the use of medications to treat symptoms, while non-pharmacological treatments involve other approaches, such as therapy or lifestyle changes. In this article, we will discuss the various pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments available for neuropsychiatric disorders.
Pharmacological Treatments
Medications are often the first line of treatment for many neuropsychiatric disorders. There is a wide range of medications available, each with its own set of benefits and risks. Here are some of the most commonly used pharmacological treatments for neuropsychiatric disorders:
- Antidepressants: Antidepressants are commonly prescribed to treat depression and anxiety disorders. They work by altering the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, which can affect mood and emotions. Some of the most commonly prescribed antidepressants include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as Prozac and Zoloft, and serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), such as Cymbalta and Effexor.
- Antipsychotics: Antipsychotics are commonly used to treat psychotic disorders, such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. They work by blocking dopamine receptors in the brain, which can reduce the symptoms of psychosis, such as delusions and hallucinations. Some of the most commonly prescribed antipsychotics include Risperdal, Abilify, and Zyprexa.
- Mood Stabilizers: Mood stabilizers are commonly used to treat bipolar disorder, a condition characterized by alternating episodes of mania and depression. They work by regulating the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. Some of the most commonly prescribed mood stabilizers include lithium, Depakote, and Lamictal.
- Stimulants: In the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), stimulants are frequently utilized. They work by increasing the levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which can improve focus and attention. Some of the most commonly prescribed stimulants include Ritalin, Adderall, and Vyvanse.
- Benzodiazepines: Benzodiazepines are commonly used to treat anxiety disorders, such as panic disorder and generalized anxiety disorder. They work by enhancing the effects of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which can reduce feelings of anxiety and promote relaxation. Xanax, Valium, and Ativan are among the benzodiazepines that are prescribed most frequently.
Non-Pharmacological Treatments
While medications can be effective for treating neuropsychiatric disorders, they are not always the best option for everyone. Some people may experience unwanted side effects, while others may not respond well to medications. In these cases, non-pharmacological treatments may be a better option. Here are some of the most commonly used non-pharmacological treatments for neuropsychiatric disorders:
- Psychotherapy: Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is a type of treatment that involves talking to a trained mental health professional about your thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. There are many different types of psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), and psychodynamic therapy. Psychotherapy can be effective in treating a wide
- Mindfulness-based practices: Mindfulness-based practices such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, and tai chi have been shown to be helpful in reducing symptoms of anxiety, depression, and other neuropsychiatric disorders. These practices can help individuals develop greater self-awareness and acceptance, as well as learn to manage stress and negative emotions.
- Exercise: Regular exercise has been shown to be beneficial in reducing symptoms of depression, anxiety, and other neuropsychiatric disorders.
- Nutritional therapy: Nutritional therapy involves making dietary changes to address specific nutritional deficiencies that may be contributing to neuropsychiatric symptoms. For example, some studies have found that increasing the intake of omega-3 fatty acids can be helpful in managing symptoms of depression.
- Light therapy: Light therapy involves exposure to bright light to treat the seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and other forms of depression. The therapy works by resetting the body’s circadian rhythm, which can become disrupted in individuals with SAD.
Overall, non-pharmacological treatments can be effective in managing symptoms of neuropsychiatric disorders. These treatments may be used alone or in combination with medication, depending on the individual’s needs and preferences.
Sign and Symptoms of neuropsychiatric disorder
Neuropsychiatric disorders refer to a group of mental health conditions that are caused by dysfunction or damage to the nervous system. The signs and symptoms of neuropsychiatric disorders can vary widely depending on the specific condition, but some common ones include:
- Changes in mood or affect: This can include depression, anxiety, irritability, or mood swings.
- Cognitive impairment: This can include memory loss, difficulty with attention or concentration, confusion, or disorientation.
- Behavioral changes: This can include agitation, restlessness, impulsivity, or changes in social behavior.
- Psychotic symptoms: This can include delusions, hallucinations, or paranoia.
- Physical symptoms: Some neuropsychiatric disorders can also cause physical symptoms, such as tremors, seizures, or movement disorders.
- Sleep disturbances: This can include insomnia, hypersomnia, or changes in sleep patterns.
- Substance abuse: People with neuropsychiatric disorders are at higher risk for substance abuse and addiction.
It’s important to note that neuropsychiatric disorders can have overlapping symptoms, and it can be difficult to diagnose them accurately without a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional. If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention.
Neuropsychiatric disorders are a complex set of mental illnesses that affect the functioning of the brain and the way people behave. These conditions range from anxiety and depression to bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. There are many different treatments available for neuropsychiatric disorders, both pharmacological and non-pharmacological. In this article, we will explore the various options for treating these disorders and their effectiveness.
Pharmacological treatments are medications that are designed to target specific symptoms of neuropsychiatric disorders. These treatments can be effective for treating symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and mood swings. Some of the most common medications used to treat these disorders include antidepressants, antipsychotics, and mood stabilizers.
Antidepressants are a class of drugs used to treat depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders. These drugs work by increasing the levels of certain chemicals in the brain, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, that are responsible for regulating mood. Some of the most common antidepressants include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as Prozac, Zoloft, and Paxil, and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), such as Effexor and Cymbalta.
Antipsychotics are a class of drugs used to treat symptoms of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and other psychotic disorders. These drugs work by blocking the action of dopamine, a chemical in the brain that is involved in regulating mood and behavior. Some of the most common antipsychotics include Haldol, Thorazine, and Risperdal.
Mood stabilizers are a class of drugs used to treat bipolar disorder and other mood disorders. These drugs work by regulating the levels of certain chemicals in the brain, such as lithium and valproic acid, that are responsible for regulating mood. Some of the most common mood stabilizers include Lithobid, Depakote, and Lamictal.
While pharmacological treatments can be effective for treating neuropsychiatric disorders, they are not without their drawbacks. These drugs can cause a range of side effects, including weight gain, sexual dysfunction, and sleep disturbances. They can also be addictive and can cause withdrawal symptoms if they are stopped abruptly.
Non-pharmacological treatments are alternative therapies that do not involve the use of medication. These treatments can be effective for treating symptoms such as anxiety, stress, and depression. Some of the most common non-pharmacological treatments include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness-based therapies, and exercise.
CBT is a type of psychotherapy that is used to treat a wide range of mental health conditions, including anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). This therapy focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to mental health problems. CBT can be conducted individually or in a group setting.
Mindfulness-based therapies are a type of therapy that focuses on teaching patients to be present at the moment and to accept their thoughts and feelings without judgment. These therapies can be effective in treating symptoms of anxiety and depression. Some of the most common mindfulness-based therapies include mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) and mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT).
Exercise is another non-pharmacological treatment that can be effective for treating symptoms of neuropsychiatric disorders. Exercise has been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression and to improve overall mental health. Exercise can be as simple as going for a walk or as complex as a high-intensity workout.
While non-pharmacological treatments can be effective for treating neuropsychiatric disorders, they are not without their drawbacks. These treatments can be time-consuming and require a significant commitment from the patient. They can also be expensive and may not be covered by insurance.
Conclusion
Both pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments are important options for individuals with neuropsychiatric disorders. The most effective approach to treatment depends on the individual’s specific condition and needs, and it is important for individuals to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan. It is also important to note that successful treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders often involves a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches.
Faq’s
- What is a neuropsychiatric disorder?
A neuropsychiatric disorder is a medical condition that affects the brain and/or the nervous system, causing a range of symptoms that affect mental health and behavior.
- What are some examples of neuropsychiatric disorders?
Examples of neuropsychiatric disorders include depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, ADHD, autism spectrum disorder, dementia, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis.
- What causes neuropsychiatric disorders?
Neuropsychiatric disorders can have various causes, including genetic factors, environmental factors, brain injuries, infections, and chemical imbalances in the brain.
- What are the symptoms of neuropsychiatric disorders?
Symptoms of neuropsychiatric disorders can vary depending on the specific disorder but may include mood swings, anxiety, depression, difficulty concentrating, memory problems, hallucinations, delusions, and impaired motor function.
- How are neuropsychiatric disorders diagnosed?
Neuropsychiatric disorders are typically diagnosed by a mental health professional, who will conduct a comprehensive evaluation that may include a physical exam, psychological tests, and discussions with the patient and their family members.






